
Warm Tip: If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Wastewater discharging from a pipe
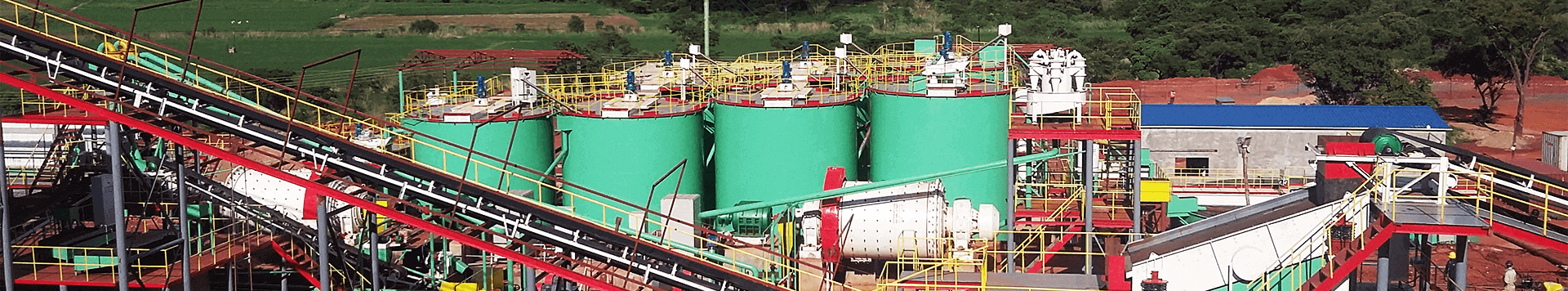
The waste water discharged from the crushing and beneficiation process of the beneficiation plant is called mineral processing wastewater. The water consumption of 1 ton raw ore is generally 4~6m³. The waste water discharged from non-ferrous metal processing plants in China is about 200 million tons per year, accounting for about 30% of the waste water from the non-ferrous metal industry.
The main sources of mineral processing wastewater in the concentrator are:
Drainage from wet dust removal in the crushing process, ground washing water for crushing and screening workshops, belt corridors and ore transfer stations;
Washing wastewater;
The cooling water of the oil cooler of the crushing and grinding equipment and the drainage of the vacuum pump;
Ground and equipment washing water from lime milk and reagent preparation workshop;
Mineral processing wastewater, including the tailings discharged from the beneficiation plant, the overflow water of the concentrate thickening pond, the filtrate of the filter of the concentrate dehydration workshop, the ground and equipment washing water from the main workshop, and sometimes overflow water of the middling thickener and the drainage from reagent removal process, etc.
The main pollutants in beneficiation wastewater are: suspended solids, acid and alkali, heavy metals, arsenic, fluorine, beneficiation reagents, chemical oxygen-depleting substances, etc.
The main hazards of pollutants in wastewater are as follows:
The suspended solids in the water mainly affects the living conditions of aquatic organisms and the photosynthesis of algae. Excessively high suspended solids may silt up the river, block the water diversion channel, and use it for irrigation will harden the soil.
As domestic water, suspended solid is annoying in the senses, and the bacteria and viruses adhere to the suspended matter is harmful to the human body.
When the suspended substance contains heavy metal compounds, under certain conditions, it will be converted into metal ions dissolved in water and cause harm.
The scientific name of xanthate is xanthogenate (RO•CS•SMe), it is a light yellow powder with a pungent odor and easy to decompose. The odor threshold value is 0.005 mg/L.
The fish and shrimps in the water bodies polluted by xanthate have an unpleasant smell of xanthate.
In addition, xanthate is unstable in water and easily soluble in water, especially easily decomposed under acidic conditions, and its decomposition product CS2 causes sulfur pollution.
The maximum allowable concentration of butyl xanthate in surface water in China is 0.005 mg/L.
The main component of dithiophosphate is dihydrocarbyl disulfide phosphate, and its impurities are formic acid, phosphoric acid, thiocresol and hydrogen sulfide. It is a dark brown oily liquid, slightly soluble in water, and has the odor of hydrogen sulfide.
It is also the source of phenol, phosphorus and other pollution in mineral processing wastewater.
The main component is terpene alcohol. Yellow-brown oily transparent liquid, insoluble in water, it is a non-toxic mineral beneficiation reagent, but has a rosin smell, so it can cause changes in the sensory performance of the water body. Because pine oil is a foaming agent, it tends to cause unpleasant foam on the water surface.
Cyanide enters human body and hydrolyze into hydrocyanic acid under the action of stomach acid, then it is absorbed by the intestines and stomach, and enters the blood.
The hydrocyanic acid in the blood can combine with the iron ions of cytochrome oxidase to generate oxidized ferric cytochrome acidase, which loses the ability to transmit oxygen, and causes tissue hypoxia, leading to poisoning.
When the concentration of CN in the water exceeds 0.1 mg/L, fish can be poisoned to death, while the lethal concentration for crustaceans is only 0.01 mg/L.
Cyanide has a self-purification effect in the water body, so this feature is often used to prolong the retention time of mineral processing wastewater in the tailing pond to meet the discharge standard.
S-, HS-in the water will affect the sanitary condition of the water body, and generate hydrogen sulfide under acidic conditions.
When the hydrogen sulfide content in the water exceeds 0.5 mg/L, it is toxic to fish and the odor emitted by it can be detected. The odor threshold value of hydrogen sulfide in the atmosphere is 10 mg/m³.
In addition, low-concentration CS2 is volatile in water and enters the human body through breathing and skin. Long-term contact can cause poisoning and lead to neurological diseases--Char-Cote carbon disulfide hysteria.
The amount of chemical oxygen-depleting substances in the water is based on the chemical oxygen demand as an indicator. Chemical oxygen demand refers to the hygienic condition of oxidizing water with a certain oxidant under certain conditions.
Excessive COD will reduce the dissolved oxygen in the water, leading to the death of organisms that require more oxygen in the water (generally referred to as fish and shrimp). Anaerobic bacteria would spread and the living water will become dead water. The higher the COD value, the more serious the water pollution.
Since the oxygen-depleting substances in the mineral processing wastewater are mainly the beneficiation reagents remaining in the water, the harmful beneficiation reagents should also be analyzed separately. It is not advisable to use only one chemical oxygen demand indicator to measure its harmfulness.
The above is the main source of the mineral processing wastewater of lead-zinc flotation plant and the hazards of its harmful components. In the next article, we will talk about how to treat wastewater to minimize its hazards and meet the wastewater discharge standards. If you have and questions, please leave your message in the form or contact online customer service directly.
Last: 3 Separation Methods for Wolframite Concentrating
Next: Treatment of Mineral Processing Wastewater in Flotation Plant
1Treatment of Mineral Processing Wastewater in Flotation Plant
 0
0
 4036
4036
24 Types of Gold Ore Froth Flotation Combined Process
 1
1
 3775
3775


What Are the Differences Between CIP and CIL?
 12210
12210
 0
0