
Warm Tip: If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
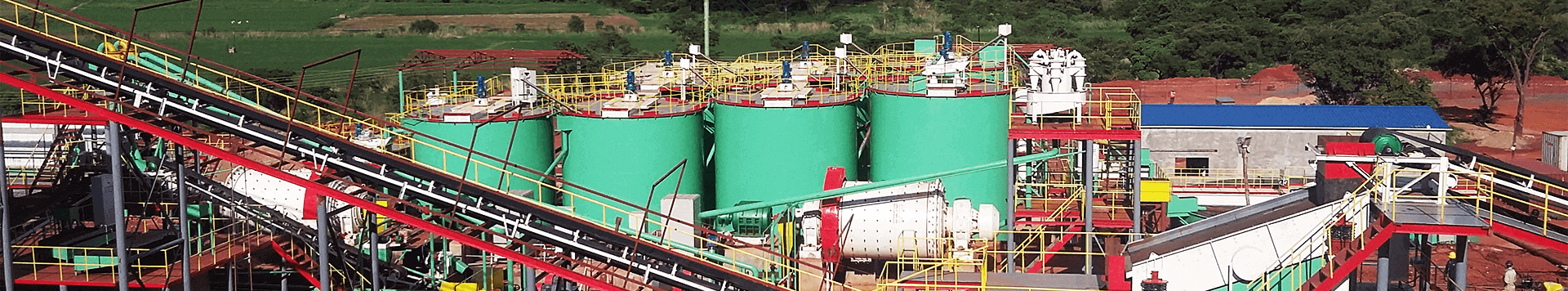
CIP all-slime cyanide carbon slurry process is developed on the basis of conventional cyanide leaching and zinc powder replacement. At present, CIP gold extraction process has achieved good technical and economic indicators. Before building a CIP gold processing plant, you must want to know how it works. This article will introduce the flow of a CIP gold processing plant: from raw gold ore to gold bar step by step.
The main process of the CIP gold processing plant to extract gold from ore and convert it into pure metal can be divided into 6 steps: crushing, screening, grinding, classification, carbon slurry gold extraction and tailings treatment.
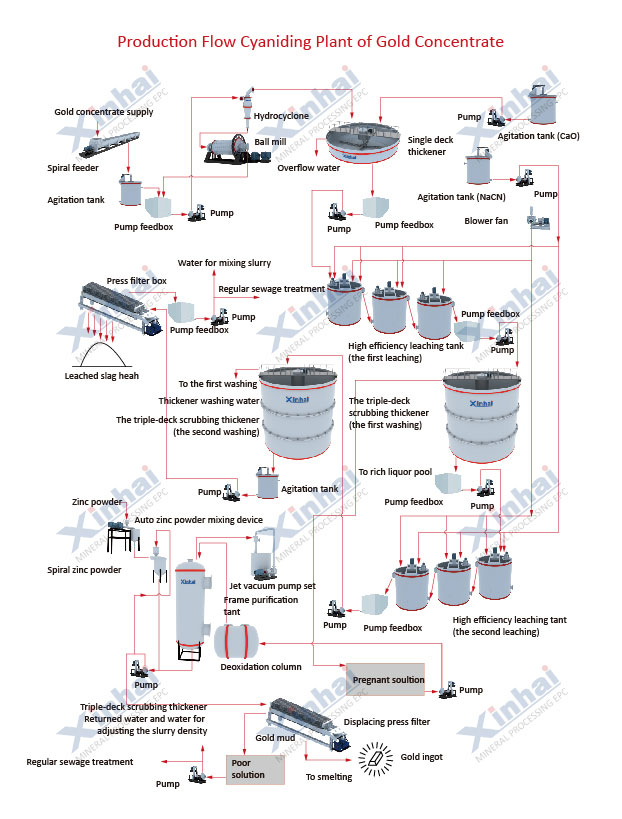
(CIP gold processing plant diagram)
The raw gold ore transported to the CIP gold beneficiation plant must first be crushed. Crushing is a process of breaking large pieces of ore into smaller-sized ore. Multi-stage crushing combined operations are often used in carbon slurry plants. And the specific application of several stages of crushing still depends on the total crushing ratio.

(Crushing process for gold ore)
Moreover, the particle size of the final crushed product should be considered in conjunction with the particle size requirements of the grinding operation to achieve the purpose of increasing the production capacity of the carbon slurry plant and reducing the total cost of the two operations of crushing and grinding.
Production practice has proved that the particle size of the final crushed product in the CIP gold processing plant is generally 10-25mm as the most appropriate. After crushing, the materials are fed into the screening equipment.
The screening operation can screen gold ore according to the particle size, increase the production capacity of grinding and improve the work efficiency of grinding, and at the same time avoid over-crushing.
Screening operations can be divided into pre-screening and inspection screening.
Pre-screening is the operation of screening the ore before entering the crusher. Through pre-screening, the qualified part of the particle size can be screened out in advance, reducing the amount of ore entering the crusher, and relatively increasing the production capacity of the crusher. In addition, it can also be used to process ores with a large mud content to prevent the crusher from clogging.
Inspection screening is performed after the ore is crushed by the crusher. The purpose is to control the particle size of the crushed product, ensure the supply of products with qualified particle size for the grinding operation, and return the oversized particles to the crushing operation to give full play to the crusher’s production capacity.
Grinding operation is the operation of reprocessing the size of the ore following the crushing and screening operation. The purpose is to dissociate useful mineral monomers and meet the particle size requirements of the carbon slurry method.
A reasonable grinding process is determined by the three most important factors: the hardness of the gold ore, the gold ore inlay, and the requirements for the particle size of the grinding product.
The grinding process of the CIP gold processing plant is the same as that of the non-ferrous metal ore. There are also one and two stages of grinding. Generally, the first stage grinding process is suitable for small CIP gold processing plants, and the second stage grinding process is suitable for medium and large CIP gold processing plants and processing fine or unevenly embedded gold mines.

(Grinding and classifition process for gold ore)
Grinding products will enter the classifying operation for the next step processing. The classification operation can divide the material into two types of products, namely "sand" and "overflow" products. According to different functions, classification operations can be divided into pre-classification, inspection classification and control classification. CIP gold processing plants mostly use a closed-circuit grinding process with inspection and classification and two processes that combine one closed-circuit, pre-inspection and classification.
After grinding and classification, the gold ore powder whose fineness is qualified enters the CIP extraction circut. The carbon slurry method is a method in which activated carbon is put into the cyanide pulp, the dissolved gold is adsorbed on the activated carbon, and then the activated carbon is electroplated to extract gold from it.
The CIP process can be divided into 5 steps: cyanide leaching, activated carbon adsorption, desorption, electrolytic deposition and carbon regeneration. Specific steps are as follows:
The CIP gold processing method generally adopts 5~8 stages of leaching, the ore grain size of the leaching tank is 80~95% -200 mesh, the leaching carbon slurry concentration is 40~45%, the cyanide concentration is 0.03%~0.05%, and the pH value is 10.5-11, the total leaching time is 24-48h.
The adsorption process is to put activated carbon into the cyanide leaching slurry to make it adsorb gold ions. Carbon adsorption generally use 4-7 stages of adsorption. In this process, an air lift or a charcoal pump is used to perform countercurrent stringing of charcoal at regular intervals. The total time of charcoal adsorption is generally 6-20h, and the gold grade of the gold-loaded charcoal is 3000-7000g/t thousand charcoal.
The CIP gold processing plant mostly uses the heating and pressure desorption method to desorb the gold-loaded carbon. The concentration of the desorption solution is NaCN 1%, NaOH 1%, the desorption temperature is 135°C, the desorption is performed at 310KPa pressure for 14-18h, and the flow rate of the desorption solution is 0.4-0.81l/s. The desorption is carried out in a closed loop with the electrowinning electrolysis operation.

(Desorption electrolysis device for gold ore)
Through electrowinning, gold is separated from the gold-loaded carbon, and then smelted and cast into gold ingots.
Through pickling and thermal regeneration methods, the activated carbon is restored to activity.
The pickling process is mainly by adding acid to make the acid react with the inorganic substances in the pores to form soluble salts, which are then washed off with water.
Thermal regeneration is to heat and desorb the carbon in a 700℃ high temperature rotary kiln, and remove the organic matter and free fine carbon on the surface and pores of the activated carbon through three stages of drying, carbonization and activation.
The cyanide-containing tailings slurry undergoes three steps of pulp concentration, cyanide reduction pretreatment and oxidation to complete the harmless comprehensive treatment, and finally dry discharge.
First, use thickening equipment to increase the slurry concentration to 50%, and the thickened supernatant is reused in the processing plant; then, the cyanide-reducing agent is added to the concentrated slurry; finally, the common oxidation method is used for oxidation.
After the harmless comprehensive treatment, the tailings of the CIP gold processing plant can be directly dry discharged.
The above is the main working process of the CIP gold processing plant. The carbon slurry process can efficiently improve the gold grade and gold recovery rate. In the actual production process, all links must be strictly controlled to maximize economic benefits. The next article is about the introduction of commonly used equipment in the CIP gold processing plant.
Last: What Are The Placer Gold Mining Methods?
Next: What Factors Will Influence Ball Mill Grinding Efficiency?
1Common Gold Extraction Methods
 0
0
 5046
5046


What Are the Differences Between CIP and CIL?
 12059
12059
 0
0