
Warm Tip: If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Gold flotation process is a kind of beneficiation method that makes the useful gold mineral adhere to the bubble to achieve gold enrichment by means of the different physical and chemical properties of the ore surface.
Gold is an easy-floating mineral, so gold flotation process has always been one of the effective ways to process gold-bearing ores. In nature, gold minerals often coexist with sulfide minerals such as pyrite, chalcopyrite, galena, and sphalerite. These minerals are both easy-floating minerals and form stable mineralized foams. They are the ideal carrier minerals for gold minerals. Gold flotation process can maximize the enrichment of gold into the sulfide concentrate. Besides, gold flotation process can be used to process pulse gold ore and alluvial gold. But since alluvial gold can be economically recovered by gravity extraction process, gold flotation process is rarely used.

Gold flotation process mainly includes the following steps:
Preparation for the ore before gold flotation process. The raw ore is crushed, screened, ground and classified (sometimes need washing and desliming) to obtain the appropriate particle size, and then enters the flotation process stage.
Add flotation reagent to flotation cell. The surface properties of minerals are changed by the action of various chemicals, the stability of the bubbles is controlled, the ion composition of the slurry is adjusted to create suitable flotation conditions, and the separation and enrichment of minerals is realized.
Agitation with aeration. The air is dispersed into bubbles by mechanical agitation, and the ore particles are sufficiently suspended and promote dissolution and dispersion of the flotation reagent.
Mineralization of bubbles. The extraction of gold can only be achieved if the selectivity of the useful mineral particles is easily adhered to the bubbles and the gangue is difficult to adhere to the bubbles.
The discharge of mineralized foam. The foam product is scraped off by a scraper or automatically spilled into a concentrate.

Gold flotation process is commonly used to process gold-bearing sulfide ore with high floatability, because the flotation process can maximize the enrichment of gold into the sulfide mineral concentrate, and the gold flotation process cost is low.
Gold flotation process is also used to process polymetallic gold-bearing ores such as gold-copper, gold-lead, gold-bismuth, and gold-copper-lead-zinc-sulfur ore. For this type of ore, gold flotation process can effectively identify and extract various gold-bearing sulfide concentrates, which is conducive to the comprehensive recovery of mineral resources.
For so-called “refractory ores” that cannot be directly extracted by amalgamation or cyanidation, it is also necessary to use a combined process including gold flotation process.
It’s difficult to use gold flotation process for extraction of coarse-grained gold ore, especially when the gold grain particle size is larger than 0.2mm.
For ore hard to reach the flotation conditions, such as quartz-bearing gold ore without sulfides, it is difficult to obtain stable flotation foam after slurring. So the performance of gold flotation process won’t be excellent.
For gold flotation process, crushing and grinding process is necessary and a huge amount of flotation reagent must be consumed. Therefore, gold flotation process means higher cost than gravity separation and amalgam treatment.
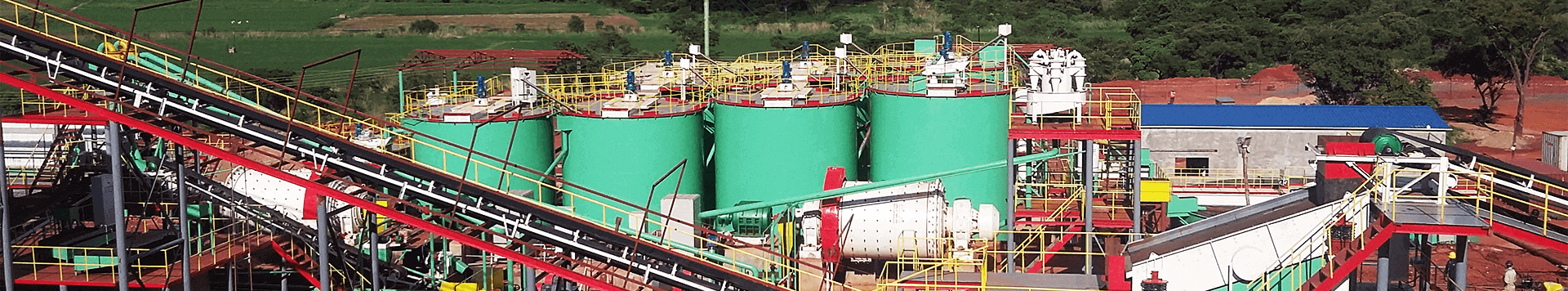
1000t/d Gold Flotation Plant in Shandong, China
Project Background
The deposit was characterized by standard minerals. There were repeated different stages of mineralization featuring an extreme low grade of sulfide. The raw ore consisted of metallic minerals (silver-gold ore, gold ore, blende, galena and hematite) and gangue minerals (quartz, sericite, feldspar, calcite, chlorite, zircon and apatite).
Process Flow
One-stage open-circuit crushing and classification + one-stage open-stage self-grinding + one-stage closed-circuit grinding and classification + flotation + concentrates dewatering
Project Result
The raw ore had an Au grade of 1.76g/t, and gold concentrates (46g/t) were produced with a gold recovery of 92%.

1Froth Flotation Analysis of Oxidized Lead-zinc Ore
 2
2
 4290
4290
2How to Choose the Froth Flotation Process According to the Flotation Stage?
 0
0
 3914
3914


What Are the Differences Between CIP and CIL?
 12246
12246
 0
0