
Warm Tip: If you want to know more details about equipment, solutions, etc, please click the button below for free consultation, or leave your requirements!
Gold-pyrite ore is a simple sulfide gold-bearing ore. If you want to recover gold and pyrite separately, you need to select the beneficiation process according to the nature of the ore. We will give a specific introduction below.
When determining the beneficiation process of gold-pyrite ore, it is necessary to understand the material composition of the ore and the symbiotic relationship of gold in the pyrite.
In general, the mineral types of this ore are simple and the content of pyrite is high. The basic feature is that gold and pyrite have a close symbiosis relationship.
In addition to pyrite, the ore may also contain a small amount of metal minerals such as galena, chalcopyrite, and pyrrhotite.
Gangue minerals are mainly calcite and quartz.
The content of pyrite is 20-45%, accounting for more than 90% of the total metal minerals.
The treatment principle of gold-pyrite ore is to separate the sulfide from the gangue and dissolve the gold in the cyanide solution. In order to remove antimony, arsenic, carbon and other substances that absorb fluoride, roasting treatment is required before cyanidation. There're 4 extraction processes.
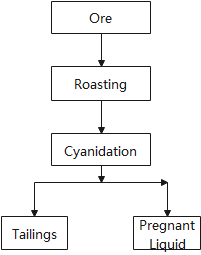
The characteristic of process I is that the ore is directly roasted and then cyanided. This process is suitable for mines with small production scale and high grade.
For example, a gold concentrator processes typical iron-gold ore, with a processing capacity of 200 tons/day and a gold grade of 10 grams/ton. All ores are calcined in a rotary calciner. The calcined ore is transported into the percolation tank with a mining cart.
Lime is directly added to the ore, and the first cyanidation time is 12 hours. The total percolation cycle time is 10 days. The gold recovery rate is 90%, the lime consumption is 0.9 kg/ton, and the NaCN consumption is 0.5 kg/ton.
#2 Flotation-Cyanidation Treatment
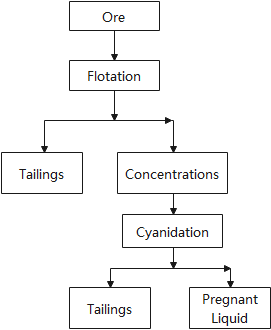
In process II, the ore is first subjected to flotation, and the flotation concentrate is then subjected to cyanidation. This process is suitable for processing ore with low iron sulfide content and free of arsenic, antimony and carbonaceous substances.
The disadvantage of this process is the low efficiency of cyanidation operation, the gold recovery rate can only reach 80-85%, and the amount of cyanide is relatively large.
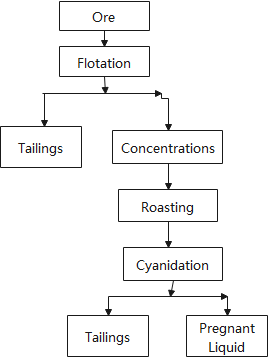
Process III is to treat the ore with flotation first. The flotation concentrates then going to be roasted, and then go to cyanidation. The characteristic of this process is that the pyrite concentrate is roasted to remove arsenic, antimony and other substances before entering the cyanidation operation, thus improving the leaching effect.
Or the flotation concentrate is roasted to produce acid, and then the gold is recovered from the calcine through gravity separation and cyanidation. This is the way to separate gold-pyrite ore in the future.
In process IV, we first treat the ore by flotation, then roast the flotation concentrate, and do cyanidation afterwards. After all these, we do a secondary cyanidation to lean liquid and tailings.
This process is suitable for processing ore that contains both non-sulfide gold and fine-grained gold encased in sulfide.
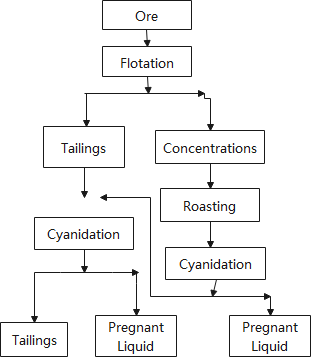
Flotation of gold-bearing sulfides and cyanidation of flotation concentrates are the common points of the above processes.
The flotation operation must first ensure that the gold is recovered to the maximum extent in the gold concentrate.
Under this premise, with the necessary number of concentrating, qualified sulfide concentrates can also be extracted. (It can be used as sulphur concentrate or gold concentrate for sale. The minimum standard for sulphur concentrate is S more than 30% and As less than 3%).
The technical measures to intensify the flotation of gold-bearing iron ore are similar to the flotation of gold-bearing quartz vein ore.
Two points are worth noting:
1) Air stirring method can improve the flotation index of pyrite and pyrrhotite.
For example, in the flotation circuit for processing copper, pyrite and pyrrhotite at a gold concentrator, the copper recovery rate is increased by 4% due to the result of aeration, and the recovery rate of gold in the pyrite and pyrrhotite has increased by 15%.
2) We can use hydrocyclone to treat flotation tailings, and then use shaking table to concentrate its sand, it is possible to obtain gold concentrates with a gold grade of 20 g/ton or more.
The cyanidation of gold-pyrite ore and its concentrate can generally be carried out under conventional cyanidation conditions.
In order to improve the leaching efficiency, stage cyanide leaching, high-concentration cyanide solution leaching and other methods can be used for treatment.
For ores containing pyrrhotite, the leaching effect is not good under normal cyanidation conditions. For this kind of ore, we should use low alkalinity cyanide solution; adding lead oxide or soluble salt for leaching; or do re-alkaline treatment and washing of the material before cyanidation.
Flotation practice has proved that because pyrrhotite is easy to oxidize, it is more difficult to float. Therefore, when the content of pyrrhotite in the raw ore is high and the relative content of gold is high, we should consider extracting it as a separate product by magnetic separation.
In actual production, we should choose the process flow suitable for our mine according to the actual situation of the mine and with the help of the technicians to achieve the highest extraction efficiency.
If you have gold-pyrite ore that needs to be separated, please contact online customer service for consultation to obtain more detailed information and targeted process selection.
If you are interested in the separation of other gold-bearing ore, we also have articles about quartz vein gold ore and gold-silver ore beneficiation, welcome to read.
14 Factors Influence the Effect of Heap Leaching Method
 5410
5410
2Common Gold Extraction Methods
 0
0
 4960
4960


What Are the Differences Between CIP and CIL?
 11932
11932
 0
0